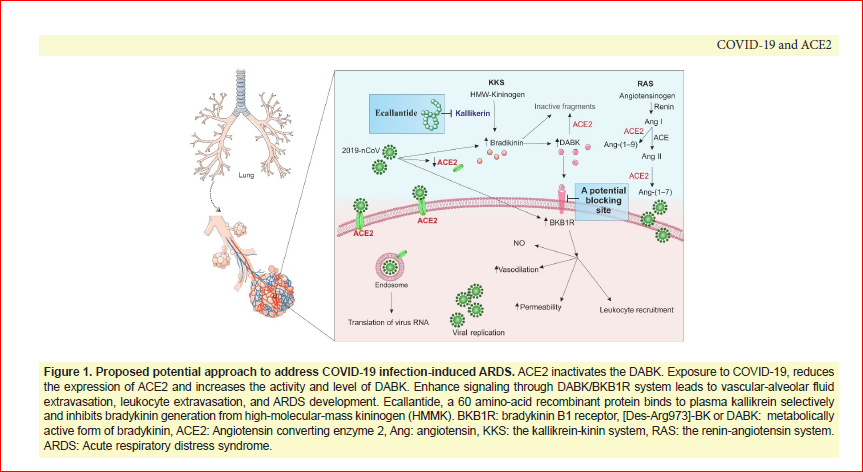
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a rapidly expanding infection around the world. The world Health Organization (WHO) in March 2020 announced the Coronavirus pandemic. This infection causes many deaths on daily basis. Therapeutic options are currently limited. It is revealed that COVID-19 binds to human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) to enter the host cells. One of the activities of ACE2 is hydrolyzing the active bradykinin metabolite [des-Arg973] BK (DABK). A decreased activity or reducing expression of ACE2 by the virus impairs the inactivation of DABK. This enhances its signaling through the bradykinin B1 receptor (BKB1R) and could lead to fluid extravasation and leukocyte recruitment to the lung. Targeting the bradykinin system by either blocking the bradykinin production or blocking bradykinin receptors may open a new potential therapeutic window for the treatment of COVID-19 induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) particularly before patients enter the irreversible stages.
Keywords: COVID-19, SARS-CoV, Bradykinin, Lung injury, ACE2, Coronavirus, Acute respiratory distress syndrome, Angiotensin converting enzyme2
 Uncategorised
Uncategorised  COVID-19 interactions with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the kinin system; looking at a potential treatment
COVID-19 interactions with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the kinin system; looking at a potential treatment Uncategorised
Uncategorised  COVID-19 interactions with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the kinin system; looking at a potential treatment
COVID-19 interactions with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and the kinin system; looking at a potential treatment




 Journals of society of diabetic nephropathy prevention follow the principles and issues of, the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE).
Journals of society of diabetic nephropathy prevention follow the principles and issues of, the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE).